|
FOREST AND GLOBAL WARMING
Forests and woodlands are an important part of our landscape and provide many benefits to society. The tree species have adapted to the local climate, atmosphere and soils over many years. However, human activities have resulted in changes to the natural environment, especially over the past 200 years. It is expected that the climate of Europe will become milder and wetter in winter, and significantly hotter and drier in the summer months over the coming century. These changes to the Earth climate are predicted to be larger and more rapid than any since the last ice-age, posing real problems for trees, woodland and forestry. The Earth's climate has changed many times during the planet's history, with events ranging from ice ages to long periods of warmth. Historically, natural factors such as volcanic eruptions, changes in the Earth's orbit, and the amount of energy released from the Sun have affected the Earth's climate. Beginning late in the 18th century, human activities associated with the Industrial Revolution have also changed the composition of the atmosphere and therefore the Earth's climate have likely influenced. For over the past 200 years, the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, and deforestation have caused the concentrations of heat-trapping "greenhouse gases" to increase significantly in our atmosphere. These gases prevent heat from escaping to space, somewhat like the glass panels of a greenhouse. Greenhouse gases are necessary to life as we know it, because they keep the planet's surface warmer than it otherwise would be. But, as the concentrations of these gases continue to increase in the atmosphere, the Earth's temperature is climbing above past levels. The Earth's average surface temperature has increased by about 1.2 to 1.4°F since 1900. Other aspects of the climate are also changing such as rainfall patterns, snow and ice cover, and sea level. If greenhouse gases continue to increase, climate models predict that the average temperature at the Earth's surface could increase from 1,2 to 4,94°C above 1990 levels by the end of this century.
THE EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING "Global warming will be the greatest environmental challenge in the 21st century." - Vice President, Albert Gore. One of the most current and widely discussed factor which could lead to the ultimate end of existence of Earth and man is global warming and its devastating effects. Scientists have asked how fast the Earth is heating up, and how the warming effects on Earth may a effect crops and climatic conditions. Several current trends clearly demonstrate that global warming is directly impacting on; rising sea levels, the melting of icecaps, and significant worldwide climatic changes. This paper will discuss the degree of destruction caused by global warming, contributing factors to warming, and finally, discuss what we can do to decrease the current rate of global warming. I would also like to present opposing viewpoints to the effects of the warming process. In my understanding, global warming represents a fundamental threat to all living things on the Earth.
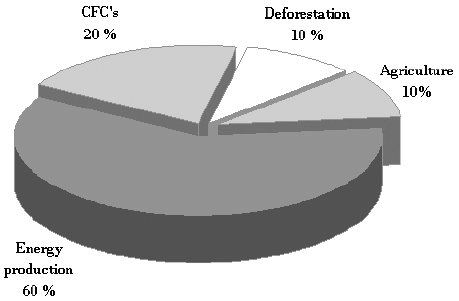
THE "GREENHOUSE EFFECT" It is important to understand and discuss the significance of global warming. Global warming is also known as the "Greenhouse effect". The "Greenhouse Earth" is surrounded bya shield of atmospheric gases, rather than a glass or a plastic cover. The air that makes up our atmosphere consists primarily of nitrogen and oxygen molecules (N2 at 78% and 02 at 21%). A large number of "trace gases" make up the remainder of air's composition. Many of these, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) are the socalled "greenhouse" gases. If you have ever felt the piercing cold of the clear winter night sky and wondered why you feel warmer on a cloudy winter night, you have experienced the atmospheric greenhouse effect firsthand. Physics tell us that any obj ect warmer than absolute zero will radiate energy. Cooler objects emit longer waves (in the infrared region) while hotter ones radiate shorter wavelengths. Our Sun, powered by its hot, nuclear fusion reaction, produces radiant energy in the visible and ultraviolet regions with relatively short wavelengths. The sunlight strikes the Earth, about 70% is absorbed by the surface of our planet and its atmosphere, while the other 30% is immediately sent back to space. If the Earth did not re-radiate most of this newly absorbed energy back into space the world would continue to get warmer. The Earth is about 33 degrees Celsius warmer than it would be if it did not have the atmospheric blanket of greenhouse gases and clouds around it. Clouds and greenhouse gases keep the earth warm. But part of the sunlight energy comes back to the Earth, creating more warming on the surface of our planet. This part of energy, which causes atmospheric gases to move back to the Earth that scientists call the "greenhouse effect". Carbon dioxide (CO2) gas generated by man's burning of fossil fuels and the forests is responsible for about half the greenhouse gas. Other gases (CFCs, methane, nitrous oxide, tropospheric ozone) are responsible for the rest. Increases in all these gases are due to mankind's explosive population growth over the last century, and increased industrial expansion. Approximately 80% of atmospheric CO2 increases are due to man's use of fossil fuels: oil, coal, and gas. Since 1945 petroleum consumption has increased dramatically, due in large part to increased usage of automobiles worldwide, and the substitution of animal power for mechanized farm machinery. Mankind is in the process of conducting a major, unintentional experiment, that of feeding back into the atmosphere in a short space of geological time the fossils fuels that have slowly accumulated over the past 500 million years. In 1958, scientists began to measure carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. The site selected for these measurements was on top of the volcanic mountain of Mauna Loa, in Hawaii. CO2 measurements at the Hawaiian site have continued. The instruments show the level of CO2 has been steadily increasing (about 0.4% per year) from a level of 315 parts per million (ppm) in 1958 to 353 ppm in 1990. Clearly, Earth's natural mechanisms for absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere cannot handle the large quantities of CO2 being added by modern man. Scientists believe nearly 1/2 of the CO2 being emitted each year remains in the atmosphere, while the rest is being absorbed by plants and the oceans.
HOW FAST IS THE EARTH HEATING UP?
Much debate in the last five years about the greenhouse effect has centered on interpreting temperature numbers generated at weather stations all over the world. The data from these thermometers are averaged and plotted in attempts to determine just how fast the earth has heated up since the measurements began. There is now no doubt the world is getting warmer. The thermometers show that the world is warmer now than at any time since the measurements started. The year 1990 was the hottest year in the last century. Together with 1991, the years of 1983,1987,1988, and 1989, have been measured to be the warmest 6 years in the last hundred years. 1991 was the second warmest year of the past century, but the volcano Mt. Pinatubo (Philippines island Luzon) erupted that year. The ash from the volcano in the upper atmosphere blocks some sunlight to the Earth, and is expected to generate a temporary two or three year cooling effect. After that time, most ash particles will have settled back to earth, and most scientists expect to see the global warming trend continue. Most scientists agree that the planet's temperature has risen 0.5 degrees Celsius since 1900, and will continue to increase at an increasing rate. The environment is responding to this warming. For instance, a study of mountain plants in the Alps (Europe), shows that some cold-loving plants are starting to move to higher and cooler altitudes. That is a possible response to increasing temperatures. .
CURRENT TRENDS The global effects of the greenhouse effect cannot be directly predicted simply because we do not have enough knowledge in the subject. However, we have been able to draw direct connections between certain natural phenomenon that supports the idea that something is changing in the climate. Global warming has great effect on crops and weather conditions around the world. The northern hemisphere contains more land area than the southern hemisphere, and conversely, a lower percentage of the world's oceans. Since oceans absorb more heat than land areas, it is not surprising that most climate models predict faster heating over the northern hemisphere than the global average. In addition, models predict faster temperature increases at higher latitudes. If global warming trends continue, high temperatures everywhere in the US may reduce US agricultural productivity. Northern continental areas are projected to have drier summer soils, due in part to earlier snow melts in the spring, and hotter, more cloudless summers, causing extensive evaporation of ground moisture. In addition, if the inland areas of the northern hemisphere are expected to receive less moisture, then, lake and river levels will be lower. Some reports predict the level of the Great Lakes (North America) will drop between 0,60 m and 2,44 m. River flows in the western US maybe very vulnerable to increasing temperatures expected as result of the greenhouse effect. When many people think of global warming, their first concern is the possible rise of sea levels. There are two major causes of rising sea levels. First, extra water is produced when ice melts. Secondly, the natural expansion of sea water as it becomes warmer. The range of sea ice around both poles continues to shrink, as it melts. Even with the level of greenhouse gases present today, the earth may warm enough in the next 50 years or so to completely melt the sea ice located on the poles. Damage from rising seas is very diverse. Buildings and roads close to the water could be flooded and they could suffer damage from hurricanes and tropical storms. There are good physical reasons to suggest that more intense storms (hurricanes) could result from global warming. Warmer oceans cause more intense storms. Experts believe that global warming could increase the intensity of hurricanes by over 50 percent. Hurricane Andrew's devastation in 1992 and hurricane Catherina in 2005 set new records. When the sea rises, beach erosion takes place, particularly on steep banks. Wetlands are lost as sea levels rise. Another serious problem is the threat of salt water intruding into underground fresh water reserves in coastal areas. In 1992, a report was published by the United Nations, which proposes that if CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions continue with present trends, the coastal plains of Bangladesh and the Netherlands will flood by the year 2100. Furthermore, the islands of the Maldives would completely disappear. This would happen if only a two foot increase in sea level occured.
FOREST DESTRUCTION CREATES MORE HEAT Trees play a unique role in the global carbon cycle. CO2 is also absorbed by the oceans and ocean organisms. Trees are able to store a large amount of CO2 in their structures. An acre (0,4 ha) of forest will absorb about 10 times the CO2 amount absorbed by an acre of crop land or grassland. One tree absorbs about 13 pounds of CO2 per year, and each one acre of forest absorbs about 2.8 tons of CO2. However, when trees are burned, the carbon locked in the structure is released into the air in the form of CO2. Today, the shrinking world forests are not able to absorb all the CO2 created by human beings while burning fossil fuels. Everyday over 5500 acres of rain forest are destroyed, and over 50 million acres are destroyed every year. Global CO2 levels rise approximately 0.4 percent each year, to levels not experienced on this planet for millions of years. Planting more trees and reducing timber cuts world-wide will help restore the imbalance, and perhaps buy time as ways are found to reduce world greenhouse gas emissions.
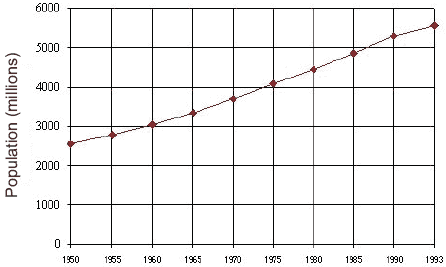
POPULATION GROWTH CONTRIBUTES TO GLOBAL WARMING The intellectual powers that we enjoy has enabled us to make effective use of technology and thereby changed the environment. Technology is partly responsible for explosive population growth and responsible for the resulting damage to Earth's resources. The industrial revolution caused a rapid increase in the population growth, as oil and gas fuels were exploited for our use. There is a clear link between the problems of global warming and overpopulation, as increases in CO2 levels follows growth in population. Presently, we have too many people on Earth, who are using technologies that are destructive for the Earth. We cannot continue to grow, and make use of limited natural resources.
ECONOMIC ASPECTS
Global warming is a big business. Some economists argue that a warmer climate could benefit certain crops and the farming communities. However, property insurers are predicting that worsening storms caused by global warming could eventually bankrupt the insurance industry. Insurance companies are now trying to form strategic alliances, and pool resources which could cover severe economic loss from climatic changes. In addition, the costs to implement a worldwide plan to cut the production of CO2 and other gases which contribute to global warming would cost approximately 3 percent of the World's total GDP. However, there is a dispute whether the industrialized world should be responsible for the main economic contributions to clean up this planet. It is important to realize that many developing nations are unable to afford actions to prevent an increase in CO2, and the fact that they have no incentive to reduce the CO2 emissions that cause the "greenhouse" effect. Several developing nations argue that the developed world was allowed to use nature in creating welfare, and that it is now morally right for them to do the same.
OPPOSING VIEW POINTS: IS GLOBAL WARMING A THREAT? Certain scientists believe that global warming is not a threat and the planet is essentially cooling off. They argue that the factors causing the phenomenon and the measurements are not fully understood, and that it is impossible to draw any conclusions whether the warming of the earth is a purely natural occurrence. These people believe that the trend is a false alarm and that it is not a sign of a forecoming global disaster. In addition, industrial forces argue that human beings can adapt to the changes caused by global warming, but they refuse to mention anything about the environmental impact of climatic changes. Other opponents to the Global warming theory believe that most changes are due to the energy of the sun which is fluctuating. Large sunspot activity is thought to be partially responsible for the "Little Ice Age" from 13th to 19th century. This climate change is well documented in history with many impacts on civilization in Europe, including famines. The temperature fluctuation was only about 2 degrees Fahrenheit. Also, some researchers believe that smoke from the burning of tropical forests and grasslands causes a strong cooling force on the climate. This cooling effect could nearly equal the warming power built by greenhouse gases created by the fires. Furthermore, in the issue regarding rising sea levels, it is important to realize that the elevations of various coastal land areas are rising and sinking due to geological factors. Thus, the ocean levels may not rise as much as we think, as continents may be sinking. In addition, some researchers believe that global warming is foreshadowing a coming ice-age. The last ice age occurred as the Earth's climate was warming. In the Arctic regions, more water would evaporate in summer, and fall onto the land as snow in winter. The winters would not be so warm as to melt all of this snow, thus glaciers would grow. Also, some carbon compounds released in the atmosphere may help prevent global warming. These particles reflect sunshine, which is redirected into space.
WHAT YOU CAN DO TO DECREASE GLOBAL WARMING? We would like to suggest several pieces of advice: First, since the largest portion of electricity in the US is produced by burning coal, we should try to cut-down on our demand for electricity. Coal combustion creates the largest amount of CO2 per energy unit of any fossil fuel. First example - coal and oil together represent 80% of the US fuel supply used to generate electricity. When we reduce electric power use, we save money, breathe cleaner air, and help to reduce the global warming problem. Every kilowatt-hour of electricity saved keeps 0,7-0,9 kg of CO2 out of the atmosphere. I believe it is time to make our lives, factories, and homes more efficient. Look around at home, and at your work place, and you will find several ways in which you can decrease the use of electricity. For instance, plant several trees on the south side of your house where they can give shade during the hot summer months. Also, install an energy efficient thermostat, with a day and night timer. Second, decrease the use of your car. If you can't afford to buy a new fuel-efficient car in the next few years, consider selling or disposing of your gas demanding car and buying a smaller, more efficient used car. Besides saving money on gas, oil, tires, parts, and repairs, you can help reduce greenhouse gases. Furthermore, no matter what type of car you drive, be sure to operate it efficiently, try to carpool to work or ride the bus, keep the car tuned up, walk or ride your bike for short distances, park and walk do not use "drive thru" services. Third, try to follow the following environmental policy of "Reduce... Reuse... Recycle." Reuse of anything is the easiest and best way to recycle. Save containers, bags, everything that you may be able to use in the future. Also, use cloth towels and napkins instead of paper ones, and use rechargeable batteries instead of disposable ones.
Al Gore on the photo from the film "An Incovenient Truth".
Unfortunately, the disbalance which we have created between our lives and the Earth is already showing the signs of disaster. "The balanced Earth" is moving to the unbalanced Earth, which, in the long run will cease to exist. Remember, we are all in the greenhouse together, nobody can stop the world like a car and get off. It is worth looking at climatic changes in two European countries: Spain and Finland, strictly speaking in their two regions: Spanish Galicia and Finnish Kainuu.
|